
 Access time plus any additional time required before second access can commence.
Access time plus any additional time required before second access can commence. 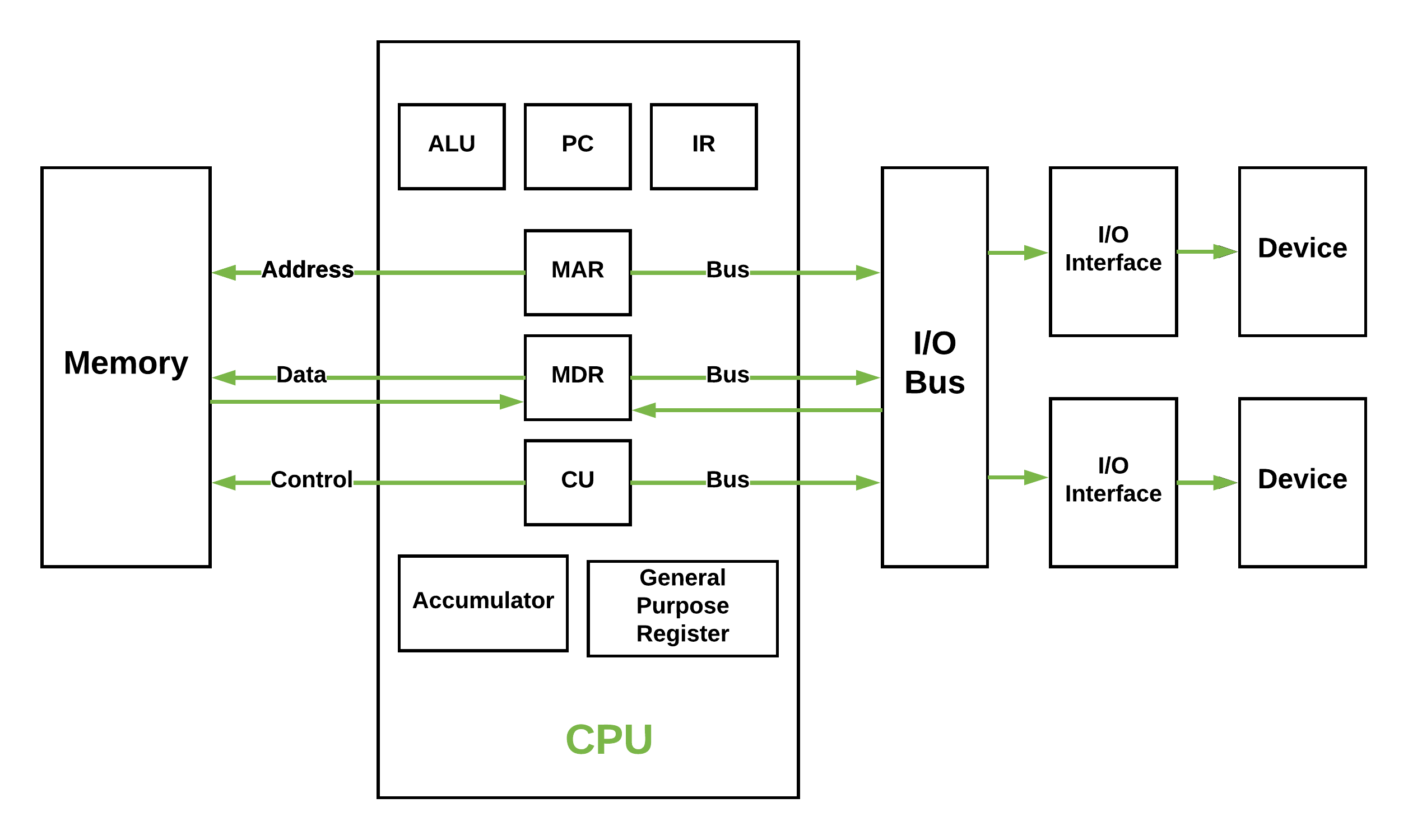 For non-random-access memory it is the time it takes to position the read-write mechanism at the desired location. For random-access memory it is the time it takes to perform a read or write operation. Main memory and some cache systems are random accessĬapacity and Performance: The two most important characteristics of memory Three performance parameters are used: Access time (latency) The time to access a given location is independent of the sequence of prior accesses and is constantĮach location has its own addressing mechanism and retrieval time is constant independent of location or prior access patternsĪny location can be selected at random and directly addressed and accessedĬache memories may employ associative access Individual blocks or records have a unique address based on physical location Memory is organized into units of data called recordsĮach addressable location in memory has a unique, physically wiredin addressing mechanismĪ word is retrieved based on a portion of its contents rather than its addressĪccess must be made in a specific linear sequence Method of Accessing Units of Data Sequential access Memory is typically expressed in terms of bytesįor internal memory the unit of transfer is equal to the number of electrical lines into and out of the memory module Refers to whether memory is internal and external to the computer Internal memory is often equated with main memory Processor requires its own local memory, in the form of registers Cache is another form of internal memory External memory consists of peripheral storage devices that are accessible to the processor via I/O controllers Table 4.1 Key Characteristics of Computer Memory Systems © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. Performance Access time Cycle time Transfer rate Physical Type Semiconductor Magnetic Optical Magneto-optical Physical Characteristics Volatile/nonvolatile Erasable/nonerasable Organization Memory modules
For non-random-access memory it is the time it takes to position the read-write mechanism at the desired location. For random-access memory it is the time it takes to perform a read or write operation. Main memory and some cache systems are random accessĬapacity and Performance: The two most important characteristics of memory Three performance parameters are used: Access time (latency) The time to access a given location is independent of the sequence of prior accesses and is constantĮach location has its own addressing mechanism and retrieval time is constant independent of location or prior access patternsĪny location can be selected at random and directly addressed and accessedĬache memories may employ associative access Individual blocks or records have a unique address based on physical location Memory is organized into units of data called recordsĮach addressable location in memory has a unique, physically wiredin addressing mechanismĪ word is retrieved based on a portion of its contents rather than its addressĪccess must be made in a specific linear sequence Method of Accessing Units of Data Sequential access Memory is typically expressed in terms of bytesįor internal memory the unit of transfer is equal to the number of electrical lines into and out of the memory module Refers to whether memory is internal and external to the computer Internal memory is often equated with main memory Processor requires its own local memory, in the form of registers Cache is another form of internal memory External memory consists of peripheral storage devices that are accessible to the processor via I/O controllers Table 4.1 Key Characteristics of Computer Memory Systems © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. Performance Access time Cycle time Transfer rate Physical Type Semiconductor Magnetic Optical Magneto-optical Physical Characteristics Volatile/nonvolatile Erasable/nonerasable Organization Memory modules 
optical disks, magnetic disks, tapes) Capacity Number of words Number of bytes Unit of Transfer Word Block Access Method Sequential Direct Random Associative

processor registers, cache, main memory) External (e.g. © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10th Edition © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
